PERIODONTICS
Periodontics is the speciality of dentistry that deals with the health of periodontium. The periodontium consists of gums, fibres bonded to the bone (periodontal ligament) and the surrounding bone.
Our team treats all issues related to periodontium professionally and successfully.
Thorough and regular oral hygiene decreases the risk of periodontosis. A check up is recommended every six months if there are no problems. On the visit soft and hard plaque can be professionally cleaned with ultrasound, teeth polished and a patient can be instructed how to brush their teeth properly.
Periodontosis is painless and without symptoms in its initial stage. If you notice bleeding and gums being swollen, increased looseness of some teeth, a permanent unpleasant smell and taste or a change in the position of the upper and lower teeth in the jaw, don’t hesitate to contact us immediately.
The main symptoms of periodontosis are:
- Swollen and red gums that bleed when teeth are brushed
- Unpleasant smell in the mouth
- Gum recession due to which teeth look bigger than before
- Wobbling teeth
- Changed position of the upper and lower teeth
- Secretion around the tooth
The main cause to periodontosis is dental plaque. Dental plaque is an invisible layer of both living and non-living microorganisms (bacteria) that adhere to the tooth surface firmly. Bacteria in dental plaque cause gum infection that is called gingivitis. Gums turn red, thick and bleed. Mineralization of dental plaque creates dental tartar.
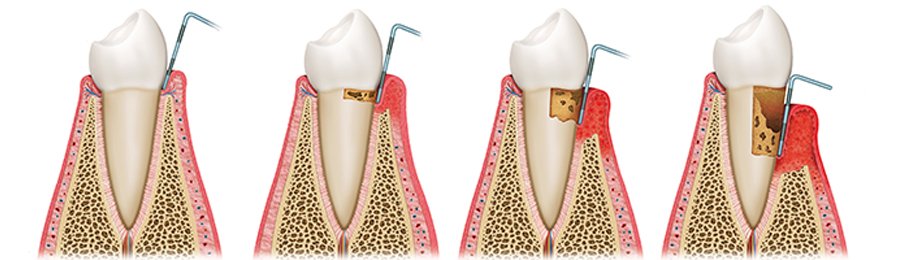
If this lasts the infection spreads deeper into the periodontal ligament, gums separate from the tooth and a periodontal pocket develops. This is the case of periodontitis. As the disease progresses the supporting bone is being reabsorbed, teeth get wobbly and a tooth can be eventually lost. Once such changes start a dental intervention is required in order to stop the process. Since worn fillings and bad prosthetic works quicken the progression of the disease quite often they need to be changed in order to achieve optimal preconditions for periodontal therapy.
Initial therapy of periodontium
Implies treatment of removing tartar, food residues, worn fillings and bad crowns edges as well as polishing all surfaces of teeth. This is quite often enough to stop the progression of the disease.
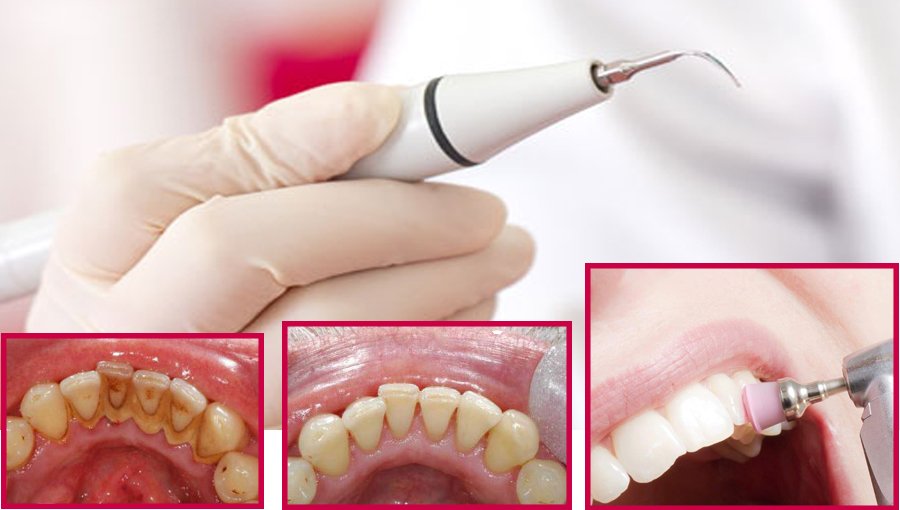
If the symptoms of the disease have not disappeared a surgical treatment is required.
A surgical therapy
Implies surgical treatments aimed at removing pockets around the tooth.
Guided bone regeneration
Treatments restore bone mass around the tooth. These treatments are provided if the progression of the disease caused major bone defects.
A corrective therapy entails surgical treatments that correct gums – the gingiva.
After periodontal therapy regular checkups are necessary.
After periodontal therapy is given the teeth can be fixed with various splints that distribute neural forces and decrease load on a single tooth. The state-of-the-art fixation system used most often fixes the teeth with a splint comprising a Reebond strap (www.ribbond.com) and composite materials.
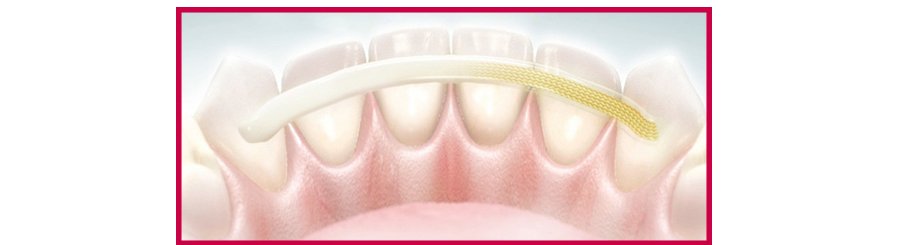
The splint is fixed on the inner surface of the teeth so it’s invisible from the outside. A splint fabricated in this way is comfortable for the patient and aesthetics is retained
Free gingival transplanted technique is taking the soft tissue in the area remote from the recession, with the aim of moving compensation, non keratinized mucosa, gingival keratinization, mostly from the area of the palate.
Problems concerning gums are far more emphasized during pregnancy as hormones affect the tissues around the teeth. Pregnant women are recommended repeated checkups, increased oral hygiene and using solutions to reduce the number of bacteria in the mouth. If necessary, professional plaque removal and periodontal therapy should be made since these protect both the health of a mother to be and her unborn child.
